What are coagulation tubes ?
Types, uses, and major differences in Blood collection tubes.
When working in the sphere of consulting and laboratory analysis, blood collectors are an essential tool. Special tubes are specifically manufactured to receive, store and preserve blood samples in order to conduct all sorts of medical tests. Each tube has various uses based on the additive contained in the tube that may include anticoagulants, clot activators or preservatives. This blog would help discover K 2 and K 3 tube, know which among the following vacuum blood collection tubes has sodium fluoride and what are coagulation tubes and a breakdown battle of blood sample collection tubes and their purpose.
What Are Blood Sample Collection Tubes?
Blood sample collection tubes are sterile plastic or glass containers used to collect blood specimens for laboratory testing. Each tube is color-coded based on the additive it contains. These additives determine how the blood sample will behave – whether it will clot or remain whole, for example.
- The typical applications of the blood collection tubes are:
- Hematology tests (e.g. CBC)
- Biochemistry tests (e.g. blood glucose, liver)
- Coagulation tests (e.g. PT, APTT)
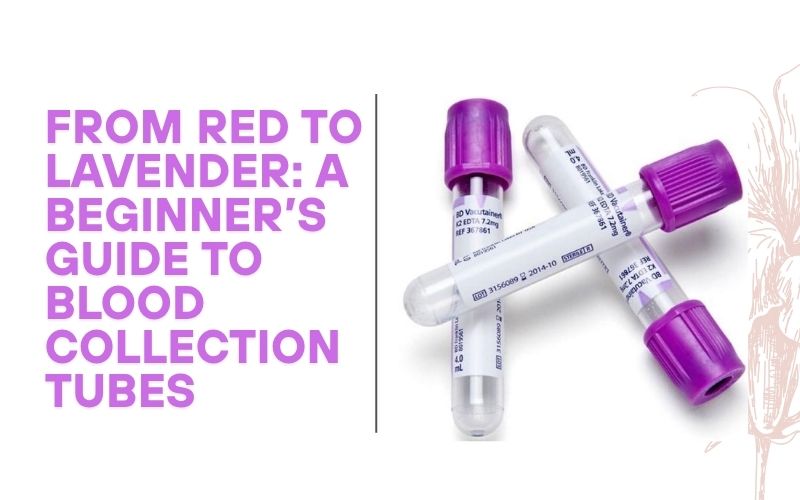
K2 and K3 Tubes: What’s the Difference?
- K2 and K3 are terms of references to EDTA tubes in hematology tests. EDTA ( Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid ) is an anticoagulant which does not allow blood to clot hence is suitable in tests that demand intact blood.
- K2 EDTA Tubes (commonly a lavender/purple top): Contains dipotassium EDTA, they are more favored in today labs because of less resultant cell shrinkage.
- K 3 EDTA Tubes: They contained tripotassium EDTA and traditionally used but might give slight distortion of blood cell morphology.
- They are needed to get proper results using complete blood count (CBC), blood grouping and other hematological analyzes.
So Which of These Vacuum Blood Collection Tubes has Sodium Fluoride?
This is a commonly asked question in lab technician exams and medical studies:
- Gray-top tube is the type of vacuum blood collecting tube which is known as the one that has sodium fluoride.
- Sodium fluoride acts as a glycolysis inhibitor and therefore it does not break down glucose in blood samples and hence retains the actual levels of glucose in the sample. They can also include potassium oxalate in the tubes and this is used as anticoagulant.
- Used for:
- Glucose in the blood testing
- Forensic laboratory blood alcohol concentrations (in forensic labs)
What Are Coagulation Tubes?
Coagulation tubes are used for blood tests that assess the clotting ability of blood. These tubes typically contain sodium citrate as an additive.
➡️ Light blue-top tubes are the standard coagulation tubes.
Sodium citrate binds calcium in the blood to prevent clotting until the sample is processed. During testing, calcium is added back to measure how the blood clots under controlled conditions.
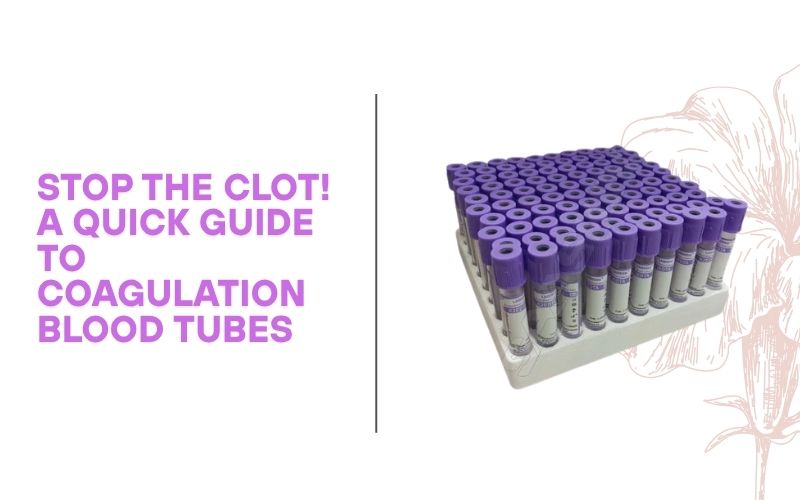
Used for tests such as:
- PT (Prothrombin Time)
- APTT (Activated partial thromboplastin time)
- D-dimer
- Fibrinogen level
Overview: Tubes used in the Collection of Blood Samples and their Applications
In short, here is what it is like:
| Tube Color | Additive | Used For |
| Lavender/Purple | K2 or K3 EDTA | CBC, Blood Smear, Hemoglobin |
| Light Blue | Sodium Citrate | Coagulation Studies (PT, APTT) |
| Gray | Sodium Fluoride + Potassium Oxalate | Glucose, Alcohol, Lactate Testing |
| Red | No Additive or Clot Activator | Serum Chemistry, Blood Bank |
| Green | Heparin | Plasma Chemistry, Ammonia, Electrolytes |
| Yellow | SPS or ACD | Blood Cultures, HLA Typing |
Have a questions? Call to us!
Mobile: (+91) – 987-180-4970,
Mail: contact@snapshophub.com



























Add comment